Exploring the Impact of Social Media on Digital Relational Anthropology
In the modern era, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, altering the way we connect, communicate, and share experiences. This transformation is particularly noteworthy in the context of digital relational anthropology, a field that examines how digital technologies shape human relationships and social interactions. As we delve into the impact of social media, it’s essential to consider both the positive and negative aspects of this phenomenon.
Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok have created vibrant online communities. These platforms enable individuals to maintain friendships across vast distances, nurture connections with like-minded people, and even forge new relationships with strangers who share similar interests. For many, social media acts as a bridge, facilitating communication that transcends geographical and social barriers. This enhanced connectivity fosters a sense of belonging, allowing users to engage in discussions, share culture, and collaborate on projects.
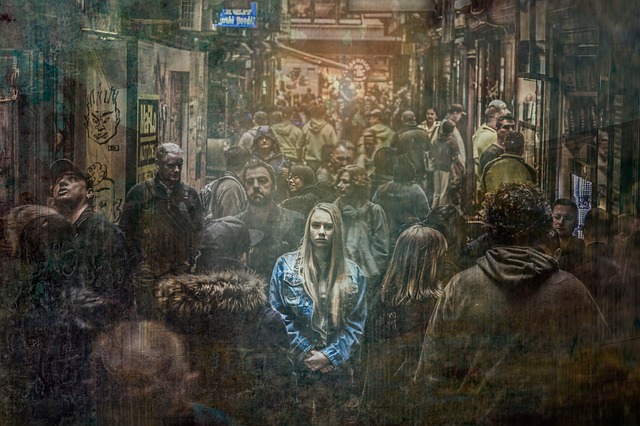
However, the very nature of social media also brings challenges that are crucial to understanding within the realm of digital relational anthropology. The curated personas we present online can lead to misunderstandings and superficial interactions. While we may appear connected to hundreds, if not thousands, of people, the depth of these relationships can often be questioned. Are we engaging in genuine relationships, or are we merely collecting followers? The impact of social media on our interactions can lead us to feel lonely, even when surrounded by others in the digital space.
Furthermore, social media has transformed the way we perceive and interact with cultural identities and social norms. Online platforms allow for the rapid proliferation of ideas, bringing diverse perspectives to the forefront. However, this rapid exchange can result in the commodification of culture, where nuanced identities are flattened into stereotypes. In examining how social media influences cultural exchange, digital relational anthropology offers valuable insights into the complexities of identity formation in our interconnected world.
The impact of social media on digital relational anthropology extends beyond personal networks; it influences societal structures as well. The power dynamics inherent in social media platforms can amplify certain voices while silencing others, thus shaping public discourse. The ability to go viral can catapult individual voices to prominence, but this fame is often fleeting and can lead to issues surrounding accountability and authenticity. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anthropologists as they navigate the shifting landscape of human interaction in the digital age.
As we continue to analyze the intertwining of social media and our relationships, it becomes clear that the influence is profound. For many, social media has redefined what it means to be connected, fostering relationships that might not have existed otherwise. Yet, this connectivity comes with an imperative to critically reflect on the quality of our interactions and the impacts on our self-perception and cultural understanding.
In this age of rapid technological advancement, engaging with digital relational anthropology allows us to explore the nuanced ways in which social media shapes our interactions, identities, and societies. Embracing the potential of social media to enrich our lives while remaining aware of its pitfalls is a delicate balance that defines our current experience in the connected world.